Run Multiple AI Sessions in Parallel with Worktrees
Learn how to use Gitton's Worktree feature to run Claude Code, Cursor, and other AI tools simultaneously across multiple branches.
Parallel AI Development with Worktrees
When developing with AI coding tools, you often have to wait for one task to complete before starting the next. With Gitton's Worktree feature, you can run multiple AI sessions simultaneously across different branches, dramatically improving your development efficiency.
What is a Worktree?
Git Worktree allows you to create multiple working directories from a single repository. Normally, switching branches requires git checkout or git switch, and you need to stash or commit your current changes.
With Worktrees:
- Open multiple branches simultaneously - Each branch has its own independent directory
- No stashing required - Keep your work-in-progress changes intact
- Enable parallel work - Develop different features at the same time
Perfect Match for AI Tools
Worktrees are especially powerful when using terminal-based AI coding tools like Claude Code, Cursor, or Aider.
Traditional workflow problems:
1. Give Claude Code instructions on feature-A branch
2. AI is working... (wait several minutes)
3. Can't do other work while waiting
4. Finally start next task after completion
Parallel development with Worktrees:
1. Create Worktree for feature-A
2. Create Worktree for feature-B
3. Open separate terminals in each Worktree
4. Run multiple AI sessions simultaneously!
How to Use in Gitton
1. Enable Worktree Feature
Enable the Worktree feature in your repository settings. Once enabled, a "Worktrees" section appears in the sidebar.
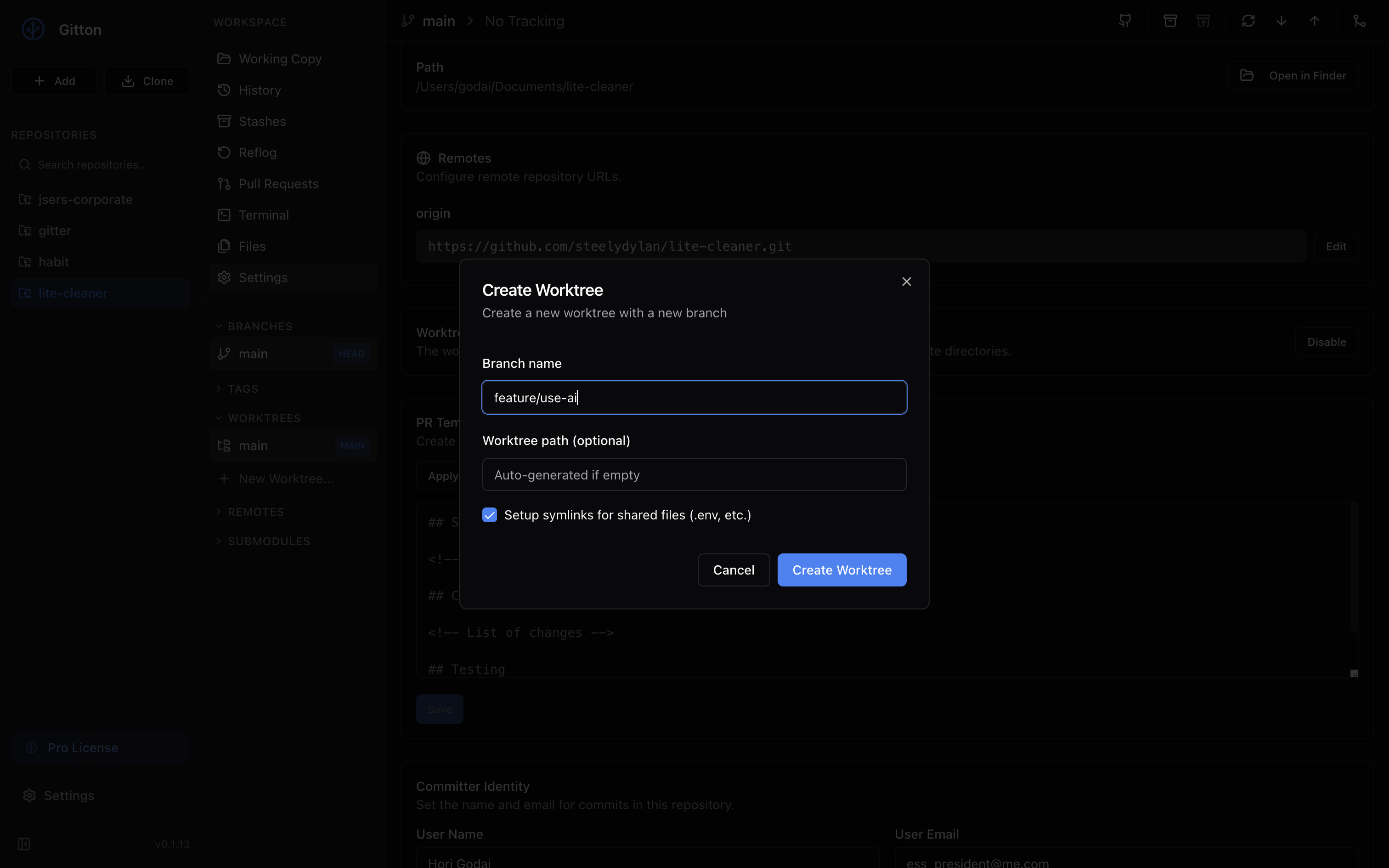
2. Create a New Worktree
Create a new Worktree from the "Worktrees" section in the sidebar.
- Branch name: Enter a new branch name (e.g.,
feature/auth-improvement) - Path: Auto-generated, but you can specify a custom path
3. Open Terminal in Each Worktree
Right-click on the created Worktree and select "Open in App" to open it as a new repository. You can then launch Claude Code in the terminal tab.
4. Give Parallel Instructions to AI
In each Worktree's terminal, assign different tasks to the AI.
Worktree 1 (feature/auth):
claude
> Add OAuth authentication to the login feature
Worktree 2 (feature/dashboard):
claude
> Implement chart visualization for the dashboard
Worktree 3 (bugfix/performance):
claude
> Improve API response performance
Automatic Environment Variable Sharing
When creating a Worktree, Gitton automatically shares important configuration files via symlinks.
Files shared by default:
.env.env.local.env.development.local.env.production.local.env.test.local
This eliminates the need to reconfigure API keys and database connections in each Worktree.
Lock Feature for Safe Work
Use the lock feature to prevent accidental modifications while AI is working on a Worktree.
- Lock: Protect Worktrees where AI is actively working
- Unlock: Unlock after completion to review changes
Practical Workflow Example
Monday morning: Parallel development of 3 features
09:00 - Create Worktrees
- feature/user-profile
- feature/notification
- feature/settings
09:05 - Launch claude in each Worktree, give instructions
09:10 - AI implementing 3 features simultaneously
↓
Check progress while enjoying coffee
09:30 - All 3 features nearly complete
Review and merge each PR
Traditional: 3 features × 30 min = 1.5 hours
Parallel: 3 features in 30 minutes!
Summary
With Gitton's Worktree feature:
- 3x+ development efficiency - Utilize waiting time effectively
- No context switching - Each task in an isolated environment
- No setup hassle - Automatic sharing via symlinks
- Safe parallel work - Lock feature prevents mistakes
In the age of Vibe Coding, parallel AI development with Worktrees is an essential skill. Give it a try with Gitton!
